Symphon-E App REST/JSON Read Access
1. Symphon-E App REST/JSON Read Access
These instructions describe read access to a Heckert Solar electrical energy storage system via the REST/JSON API. Then, the interface’s functionality is explained.
1.1. Prerequisites
The device accessing the electrical energy storage system (e. g. notebook/PC) must have direct access to the IP address of the EMS — e. g. be connected to the same physical network.
1.2. REST/JSON basics
The REST/JSON interface enables access to the EMS in the local network via an interface based on REST .
1.3. Read access
This app provides an interface based on REST that can be used to read data points in the system.
| This app is included in the EMS standard scope of delivery. |
The base address for REST access is http://<USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>:80/rest
-
httpis the protocol -
<USER>is the user name. As authentication only takes place via the password, any value (e. g. "x") can be entered here -
<PASSWORD>is the password of the user. The default "guest" user in EMS has the password "user" -
<IP>is the IP address of EMS -
80is the port for the REST/JSON API (optional)
So if your EMS has the local IP address '192.168.0.23', the base address for REST access is http://x:user@192.168.0.23:80/rest
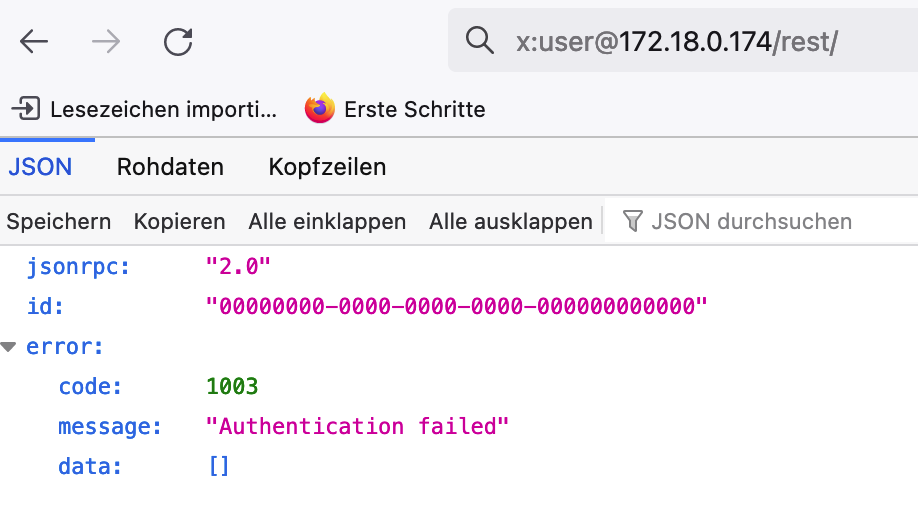
| For security reasons, Simple Authentication Requests are not supported, as passwords are transmitted via the URL in this variant. Header authentication must be used explicitly for REST calls. A query directly via the browser (without an extension) is therefore not possible. In this case, an error message appears, see figure Error message for Simple Authentication Requests. For a query in the browser, please use the Talend API Tester extension as described in here. |
1.3.1. /channel endpoint
The /channel endpoint enables access to individual data points, so-called "channels", in the system.
The full address of the endpoint is:
http://x:<PASSWORD>@<IP>:80/rest/channel/<COMPONENT>/<CHANNEL>
1.3.2. Data points
The following data points of the _sum component can be read out:
Data point |
Description |
Unit |
State |
0: Ok, 1: Info, 2: Warning, 3: Fault |
|
EssSoc |
State of Charge |
Percent [%] |
EssActivePower |
AC-side active power of the electrical energy storage including excess DC generation with hybrid inverter |
Watt [W] |
EssReactivePower |
AC-side reactive power of the electrical energy storage |
Volt Ampere Reactive [var] |
GridActivePower |
Active power at the grid connection point |
Watt [W] |
GridMinActivePower |
Minimum active power ever measured at the grid connection point |
Watt [W] |
GridMaxActivePower |
Maximum active power per measured active power at the grid connection point |
Watt [W] |
ProductionActivePower |
Active power of the PV yield and, if applicable, yield from external inverters |
Watt [W] |
ProductionMaxActivePower |
Maximum measured active power of the PV system |
Watt [W] |
ProductionAcActivePower |
Active power of the external AC inverters |
Watt [W] |
ProductionDcActualPower |
Power of the DC generation of the hybrid inverter |
Watt [W] |
ConsumptionActivePower |
Active power of the electrical consumption |
Watt [W] |
ConsumptionMaxActivePower |
Maximum active power of the electrical consumption ever measured |
Watt [W] |
EssActiveChargeEnergy |
Cumulative electrical energy of the AC-side battery charging incl. excess PV generation at the hybrid inverter |
Watt hours [Wh] |
EssActiveDischargeEnergy |
Cumulative electrical energy from electrical energy storage to consumption via AC output of the inverter incl. PV generation |
Watt hours [Wh] |
GridBuyActiveEnergy |
Cumulative electrical energy of grid consumption |
Watt hours [Wh] |
GridSellActiveEnergy |
Cumulative electrical energy of grid feed-in |
Watt hours [Wh] |
ProductionActiveEnergy |
Cumulative electrical energy of PV generation + external inverter generation |
Watt hours [Wh] |
ProductionAcActiveEnergy |
Cumulative electrical energy of the external inverters |
Watt hours [Wh] |
ProductionDcActiveEnergy |
Cumulative electrical energy of the PV generation of the inverter |
Watt hours [Wh] |
ConsumptionActiveEnergy |
Cumulative electrical consumption |
Watt hours [Wh] |
EssDcChargeEnergy |
Cumulative DC electrical energy of battery charging |
Watt hours [Wh] |
EssDcDischargeEnergy |
Cumulative DC electrical energy of storage discharge |
Watt hours [Wh] |
EssDischargePower |
Actual AC-side active power of the electrical energy storage |
Watt [W] |
GridMode |
1: On-Grid, 2: Off-Grid |
1.3.3. Example 1 — Querying the state of charge: cURL
The command line program cURL is pre-installed on both Windows and Linux.
To read out the state of charge of the electrical energy storage, send a GET request to the address: http://x:user@192.168.0.23:80/rest/channel/_sum/EssSoc
You will receive a response in JSON format:
Windows
The following command saves the response in JSON format in the out.json file
>curl -o out.json http://x:user@192.168.0.23:80/rest/channel/_sum/EssSocTo output the contents of the file, use :
>type out.jsonOutput:
{"address":"_sum/EssSoc","type":"INTEGER","accessMode":"RO","text":"","unit":"%","value":99}The state of charge value is found under value. In the example above, it is 99 %.
Linux
The following command saves the response in JSON format in the out.json file
$curl -o out.json http://x:user@192.168.0.23:80/rest/channel/_sum/EssSocTo output the contents of the file, use :
>cat out.jsonOutput:
{"address":"_sum/EssSoc","type":"INTEGER","accessMode":"RO","text":"","unit":"%","value":99}The state of charge value is found under value. In the example above, it is 99 %.
1.3.4. Example 2 — Querying the state of charge: Python
Python versions for Windows and Linux are available here: https://www.python.org/downloads/
To read out the state of charge of the electrical energy storage, a GET request must also be sent to the address:
http://x:user@192.168.0.23:80/rest/channel/_sum/EssSoc must also be sent.
The requests library, which must be imported at the beginning, can be used for this:
import requests
url = 'http://192.168.0.23:80/rest/channel/_sum/EssSoc'
user = 'x'
password = 'user'
session = requests.Session()
session.auth = (user, password)
response = session.get(url)
response.raise_for_status()The command returns a response in JSON format. Output it using the following command:
print(response.text)Output:
{"address":"_sum/EssSoc","type":"INTEGER","accessMode":"RO","text":"","unit":"%","value":99}The state of charge value is found under value. In the example above, it is 99 %.
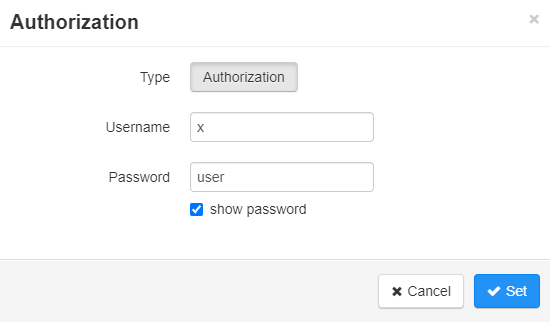
1.3.5. Example 3 — Querying the state of charge: Talend API Tester
Talend API Tester is an extension for Google Chrome that allows to test REST APIs.
First, an Authorization header must be added:
Then, execute the GET request.
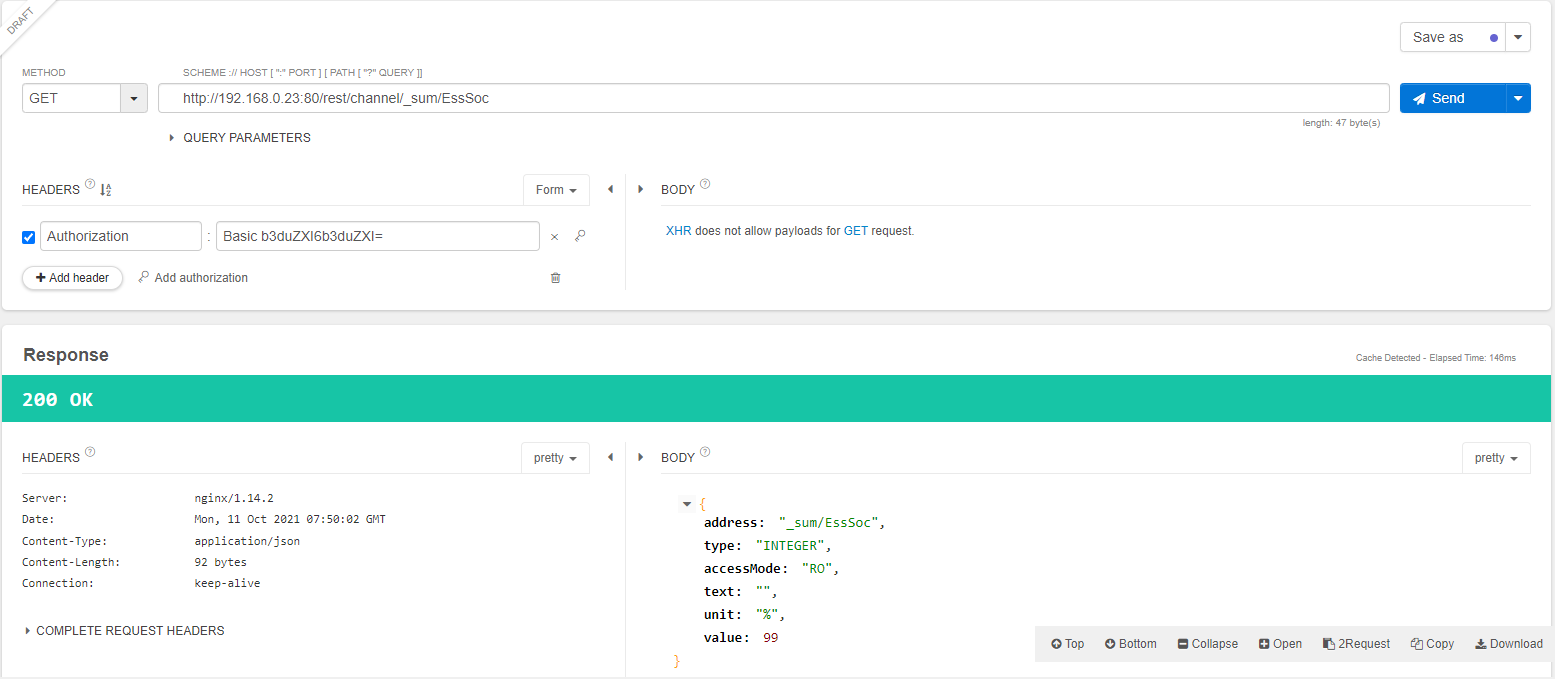
The state of charge value is found under value. In the example above, it is 99 %.